Highlights
- What is 3D printers
- How to use 3D Printers
- Pick the best 3D printers on the following parameters.
- Top 5 3D printers of 2023
- The future importance of 3D Printers
No doubt, 3D printers are the future and a part of the future. Learn about the best 3D printers of 2023 according to different organization sizes and more.
Introduction
The way the world is revolving around technology, 3D printers are just getting started with their potential to reign.
With the tight competing market there are some of the best 3D printers that ticks almost all the right boxes, providing good printing quality, uninterrupted Wi-Fi connection, Strong Software, and many other aspects.
Besides this, get to know what a 3D printer is, how it works, the best 3D printers in 2023 with its pros and cons, and much other information pertaining to it.
What is a 3D Printer?
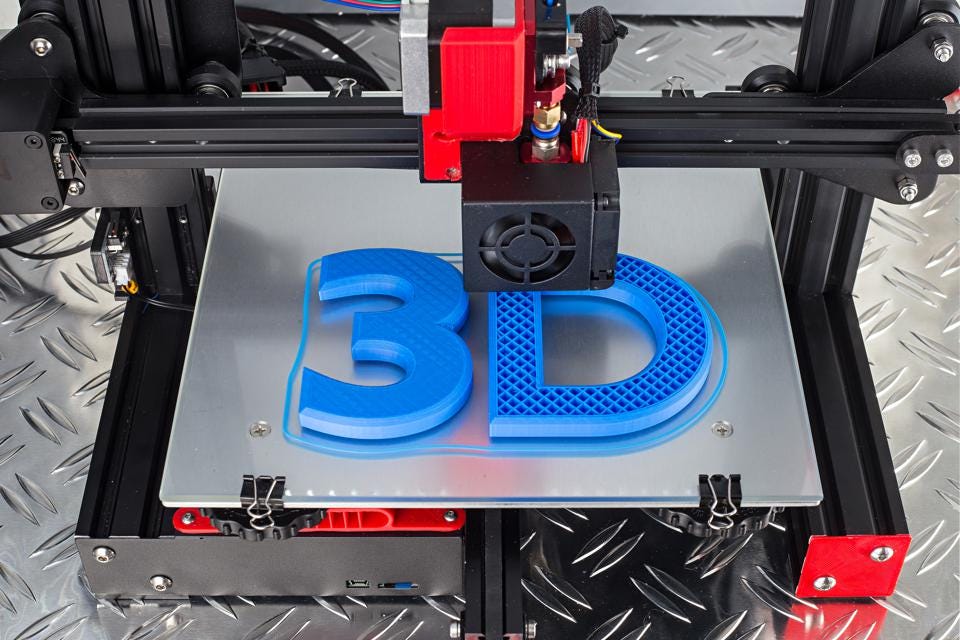
3D printing also called Additive manufacturing is a smart method of constructing 3D objects from the digital 3D model.
The processes are numerous, where material, such as plastics, liquids or powder grains are fused layer by layer to solidify the object created under device control.
The growing adoption of 3D printing or additive manufacturing across diverse industrial verticals to get a three dimensional solid project from the idea extracted from the digital files. Additive processes help in creating 3D printed objects.
The successive layers of material are laid down until the object is created via additive process. These layers are seen as fine sliced sectioning of the object.
Previously, down a decade 3D printing techniques were cautiously used to generate aesthetic or functional prototypes, more of a rapid prototype.
However, by 2019, with the development, advancement, and precision in 3D printing techniques, this technology became a vital element as an industrial-production technology.
In comparison to the conventional manufacturing methods, 3D printing directs to create complex shapes, geometries, and objects, without consuming excess from the limited resources and that seem to be difficult to construct manually, which adds to the growth inducing factor of the market and intrigue for the same.
How does the 3D Printer work?
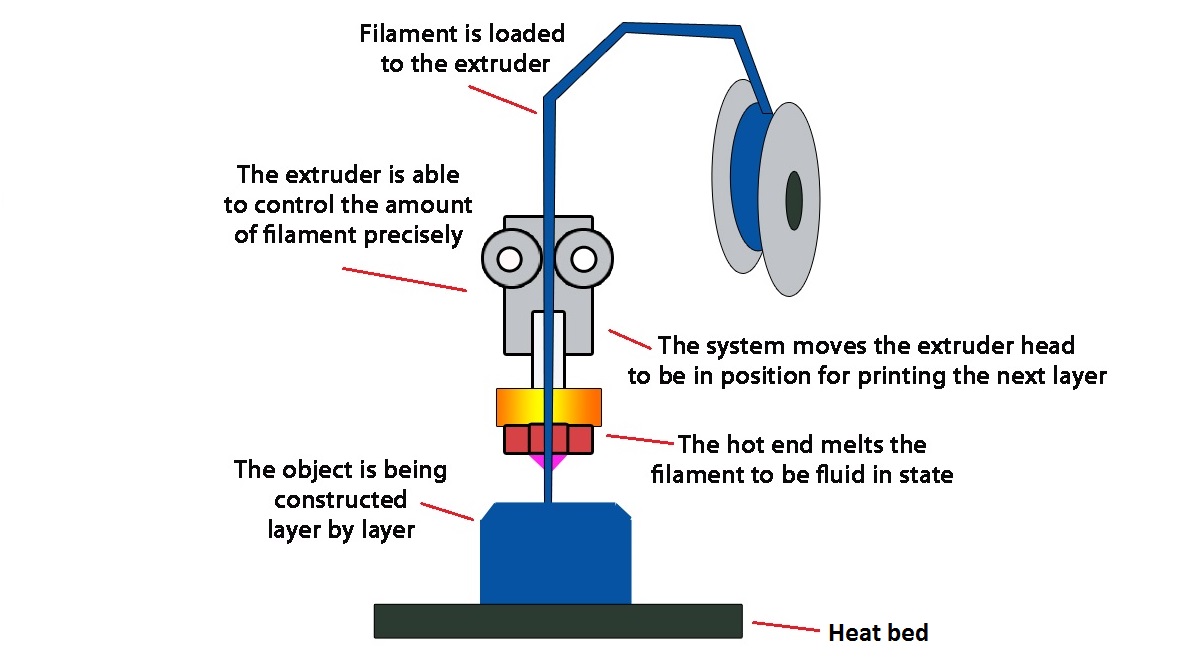
As said before, 3D printing is additive manufacturing, where the 3D objects are created by using material, usually plastic.
Following the printing method as similar as traditional inkjet printers, but only in 3D. Additive manufacturing creates any complex to easy objects in layers, by continuously adding material until the object reaches to its final design and molding is completed.
3D printers can only be used after accomplishing a digital design for the production of an object. Once achieved, 3D printers build the structure according to the computer-aided design.
This process entails updated software, precision tools, and powder-like materials to build the 3D object from ground.
The Process Involves the Following Steps
Step 1: 3D Modeling Software
3D modeling is the first step that implies designing the object on the device for high end precision.
Each object should be designed first via 3D modeling software and the designs can be as intricate and exact as possible for 3D printers to build.
Each sector can use the 3D modeling software to pay attention to the minute details and generate precision and exactness of the object.
The software levels up the game for the computer-aided designs to lay perfectly in 3D designing and customize the design accordingly.
Step 2: Slicing the Model
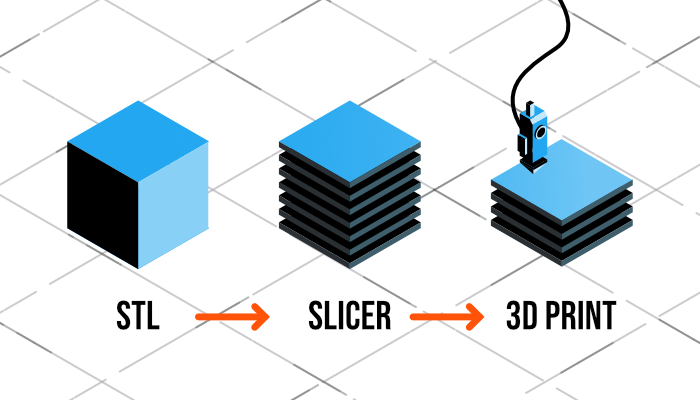
Next step is slicing, where engineers slice the one big model into layers to print and create the final product. The conceptualization method for 3D printers requires the slicing software to scrutinize each layer of a model and recreate the layers according to the printer.
There is also a ‘fill’ feature in a slicer that commands the 3D printed object to solidify the internal columns where required. Once done with slicing, the model is finally moved to execute the actions.
Step 3: The 3D Printing Process
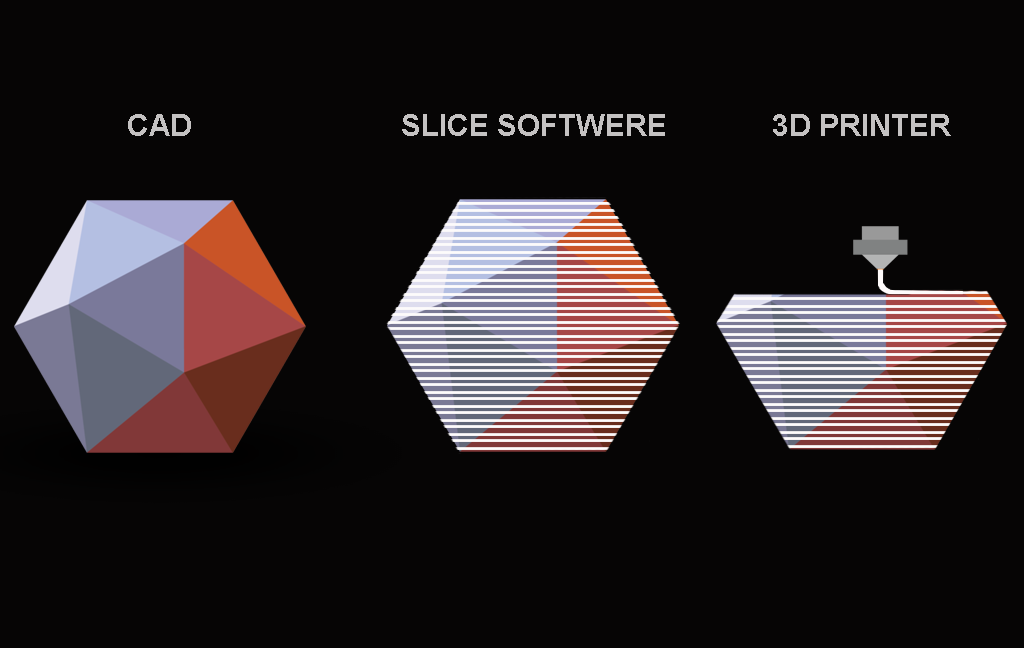
After being done with modeling and slicing the object for 3D printers to finally take the lead, it appears to operate the same as the traditional inkjet printer.
As the ebb and flow of the nozzle takes place layer by layer dispensing a wax or plastic-like polymer. The next layer is only added when the prior added layer is dried.
Different Printing Materials
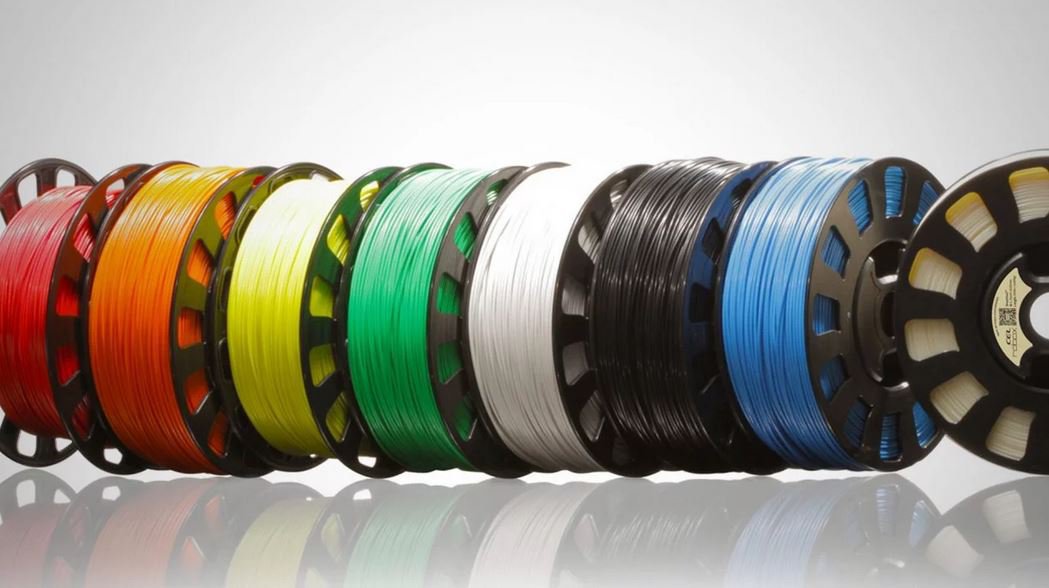

The 3D Printing Materials coming together that creates the 3D object, includes
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS): Plastic material that is tough to break but easy to mold according to the object.
Carbon Fiber Filaments: lightweight filaments that also create strong objects.
Conductive Filaments: Printable material used for wearable technology as it can be used to print electric circuits without requiring wires.
Flexible Filaments: Filaments that help in creating bendable yet tough objects. Can produce
Metal Filament: made of ground metals and polymer glue, available in steel, brass, copper , and bronze to produce the metal object with true look.
Wood Filament: The filament is made of polymer glue that is finely mixed with ground wood powder to produce wooden-looking objects.
Processes and Techniques of 3D Printing

There are some of the techniques of 3D printing used widely across diverse sectors. The techniques are as follows:
Stereolithography (SLA) Technology
SLA technology is used to create intricate and detailed objects, as well as supports fast prototyping printing. An ultraviolet laser is used to produce the objects in less time.
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
FDM technology is among the vastly adopted technologies for 3D printing. Majorly used to create the models and prototypes with plastic.
Digital Light Processing (DLP)
DLP technology uses lamps to generate the prints at higher speed as compared to SLA printing, as it allows the layers to dry in no time. It is also the oldest form of 3D printing.
Material Jetting
Material jetting technique uses droplets of material by small diameter nozzle to build a layer- to- layer platform, the object becomes strong due to the UV light used.
Continuous Liquid Interface Production (CLIP)
The CLIP method uses Digital Light Synthesis technology to preview the sequence of UV images for the cross-section 3D printed part.
This method enables the curing process to have precise control. This process causes numerous chemical reactions that allow the layers to harden.
Binder Jetting
For Binder Jetting technique powder base material is used along with the liquid binder that act as an adhesive for the powder particles and are released via jet nozzles.
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
FDM is also known as Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF). This technique works by unwinding a plastic filament that flows through the heated nozzle in vertical and horizontal directions. This way it immediately forms the object by hardening the melted material.
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
SLS technique works by fusing small particles of powder together via high-power laser to build 3D objects. The laser scans the layers formed via powderbed and selectively fuses them, which lowers the powder bed by one layer and repeats the process until getting the desired thickness.
Multi-Jet Fusion (MJF)
MJF is another form of Powder Bed Fusion as it uses a sweeping arm that enables the deposit of powder and the application of inkjet-equipped arm for selective binding.
Moreover, there is a detailing agent that is used for the precision of the object. Also, there is utilization of thermal energy to cause the chemical reaction.
Directed Energy Deposition
Majorly used in the metal industry, Directed Energy Deposition technique operates on the 3D printing apparatus attached to a nozzle for applying the powder and a multi-axis robotic arm.
The application of the powder on the surface and energy source that melts the material that creates solid objects.
How to choose the best printer for your business?

Any business choosing the right 3D printer is based on a few parameters. The parameters for the same are as follows:
Printer type
There are two types of 3D printers, including FFF (fused filament fabrication) and SLA (stereolithography).
FFF printers work by melting and molding plastic filament to create the object with a moving printhead.
Whereas, SLA printers employ UV lasers to harden the resin that solidify the model.
FFF printers are relatively cheaper than the SLA printers, not only cheaper but easy to use and simple.
Printing Materials
The printing material varies for each type of printer.
FFF filament material includes PLA (a brittle, biodegradable material), HDPE (a light, tough polystyrene), ABS (the same plastic used in Lego blocks), and TPE (a soft, rubberlike material). Where the availability of PLA and ABS are in various colors and hues.
SLA printers comparatively function on fewer options.
However, the SLA printers are well equipped to form the objects from very rigid to rubbery.
The best 3D printers are those that can apply a wide range of material to form an object with desired degree of rigidity.
Note that: There are some 3D printers that allow the use of some material that is approved and produced by the respective manufacturer of the printers.
Print Volume
Determine the print volume before buying a 3D printer. As all printers come with certain limits on the basis of size of the object can be created.
The print bed decides the size of the print, which is measured by the cubic inches. Also look into the individual dimensions to ascertain the production of the maximum size 3D print.
Print Speed and Quality
Currently, 3D printing requires time to create the object, as produced in layers and the model design can vary from simple to complex.
The typical 3- to 4-inch design takes around 6 and 12 hours to create the object. Thicker the layers, quicker the print. The speed is also based on the print quality of the object.
Price
The 3D printers used by professional designers and creators can be of a heavy price.
However, the best 3D printers can also come at a budget-friendly price.
For the same read ahead to the top best 3D printers of 2023 that will be economical too.
Note that: There are some 3D printer producers that do not enroll their product on Amazon or any e-commerce platform. The users can also buy the product directly through the company;s website as well.
Top 5 3D Printers of 2023
Monoprice Voxel
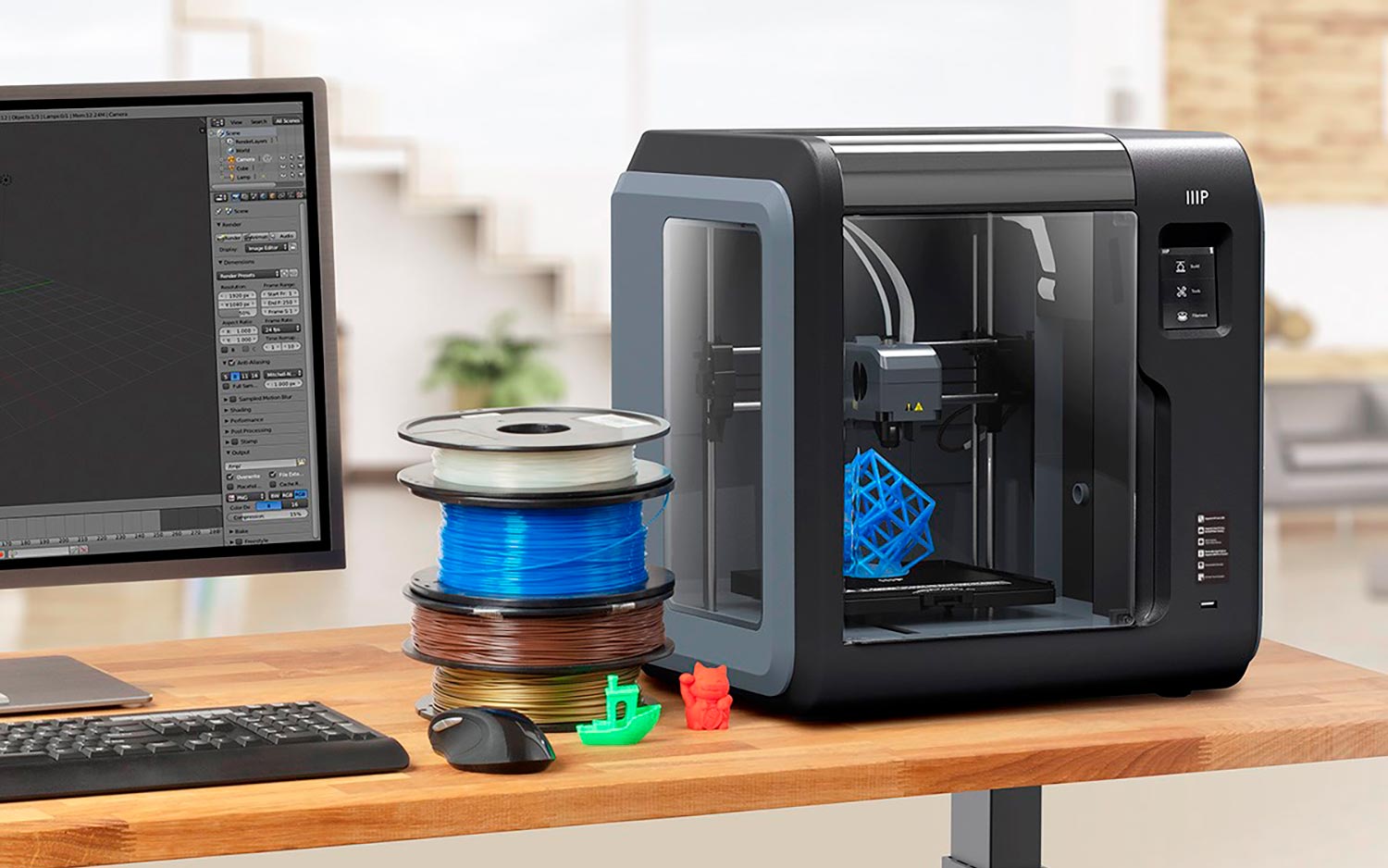

Monoprice Voxel 3D printer, not too expensive as a 3D printer and do the task with presion.
This printer produces high quality prints and doesn’t hit the pocket badly as it is priced at Rs. 30,463.00.
Beginners can choose this printer as it can produce reliable prints by using ABS material and due to the heated print base on Monoprice Voxel.
The print bed’s top slides out and is flexible catering to remove prints fast.
Voxel can be a good choice for home or a classroom to meet the objective of the purchase.
SPECIFICATIONS
Printer Type: FFF
Layer Resolution: 50 to 400 microns
Materials: ABS, PLA, Wood Fill, Copper Fill, Steel Fill, Bronze FillBuild Volume: 6.9 x 6.9 6.9 inches
Printer Size / Weight: 15.9 x 15.7 x 15 inches / 19.8 pounds
| PROS | CONS |
|
|
Priced at: Rs. 30,463.05
Prusa Mini+
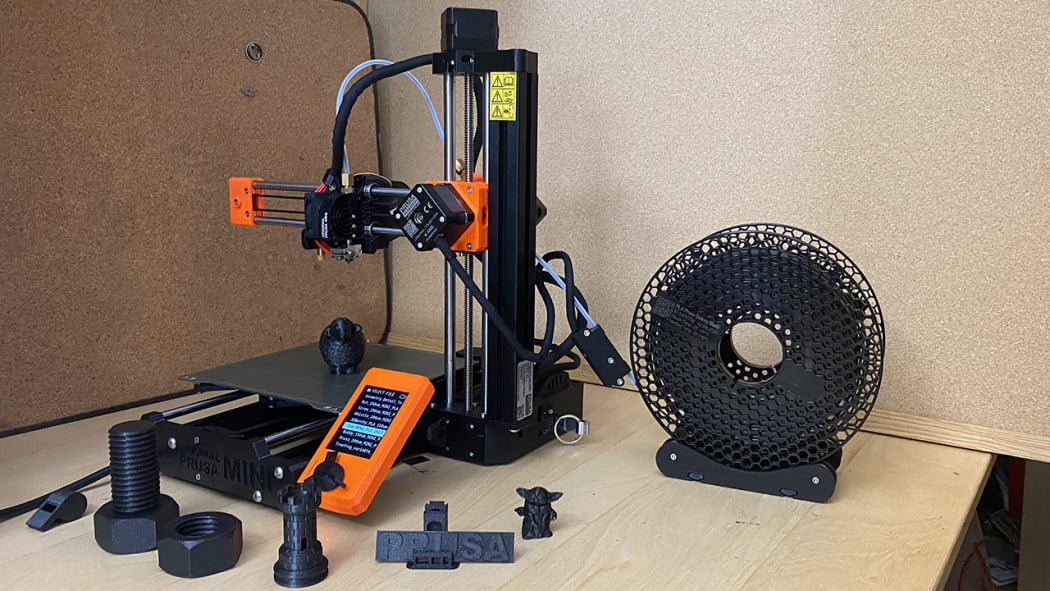

The Prusa Mini+ 3D printer can be the just the right fit for many beginners as it produces an excellent print quality and offers maximum reliability.
However, it is more expensive than its counterparts as it will be priced at Rs. 40,000.
Practically speaking, the Prusa Mini+ 3D printer is easy to set up but doesn’t have an enclosed printing space, which can be a problem if set around children.
The printer has a top-notch software prone to produce good quality objects from the model provided.
Moreover, the print speed is fast at 0.2mm quality print mode. Along with the material used in the printer it also makes the printer a reliable choice.
SPECIFICATIONS
Printer Type: FFF
Layer Resolution: 0.05 to 0.25 mm
Materials: PLA, PETG, ABSBuild Volume: 7 x 7 x 7 inches
Printer Size / Weight: 15 x 13 x 12.6 inches / 11 pounds
| PROS | CONS |
|
|
Priced at: Rs. 40,000
Formlabs Form 3+
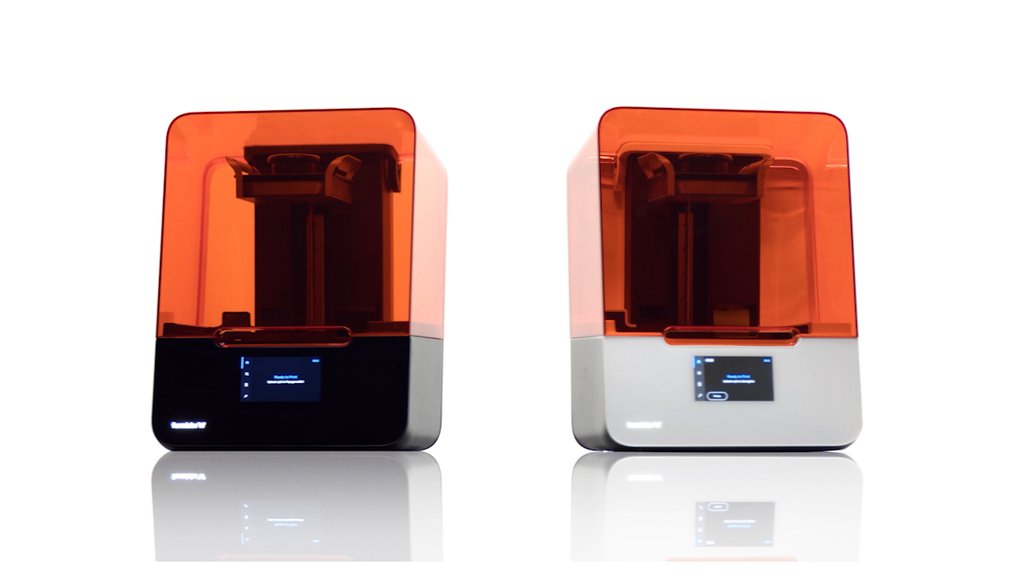

Coming with a host of things, including Form 3+ 3D Printer, Form 3 Resin Tank V2.1, Build Platform, and Form 3 Finish Kit.
Formlabs Form 3+ printer will be priced at $3,750.00.
Resin based, SLA Form 3+ printer can be part of the regular workflow. This new version comes with better printing and easier to use.
Resin setup is also an easy task as well as the floating level sensor provides the exacts of the resin present in the tray.
Flexible build platform ensures the simplified task of removing prints.
Along with the advanced software system the printer can be a good pick.
SPECIFICATIONS
Printer Type: SLA
Layer Resolution: 25 to 300 microns
Materials: Resin
Build Volume: 7.3 x 5.7 x 5.7 inches
Printer Size / Weight: 20.9 x 15.9 x 14.8 inches / 38.5 pounds
| PROS | CONS |
|
|
Priced at: $3,750.00
Photon Mono X
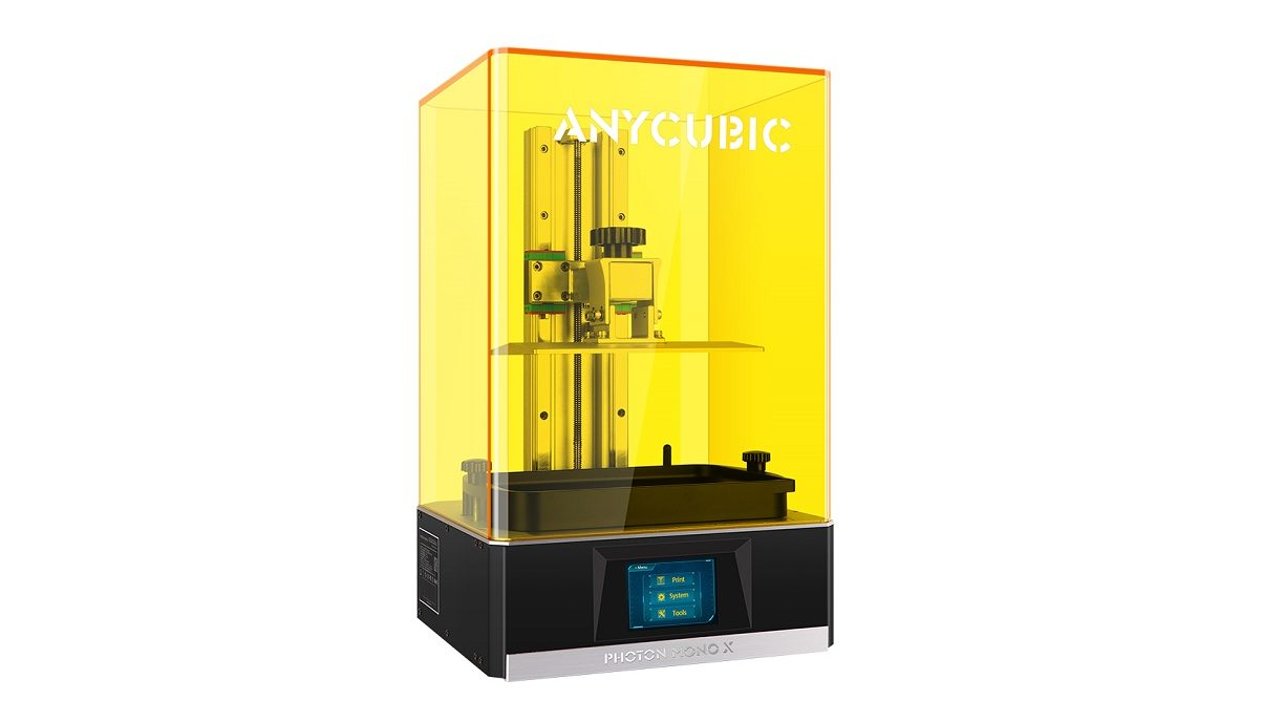

Possibly the best pick for a budget-friendly SLA printer, as Photon Mono X is priced at Rs. 45,000. Compared to the Form 3, Photon Mono X is way more reasonable.
The results are also more than impressive and creates high-quality SLA prints, despite the sporadic printing error.
With the printing area of 331 cubic inches, providing a large printing area that can be a good-fit home workshop or small organizations.
And have no restriction on approving the resin.
SPECIFICATIONS
Printer Type: SLA
Layer Resolution: 0.01-0.15mm
Materials: Resin
Build Volume: 9.6 X 7.5 X 4.6 inches
Printer Size / Weight: 18 X 11.4 X 10.6 inches / 23.7 pounds
| PROS | CONS |
|
|
Priced at: Rs. 45,000
FlashForge Adventurer 4
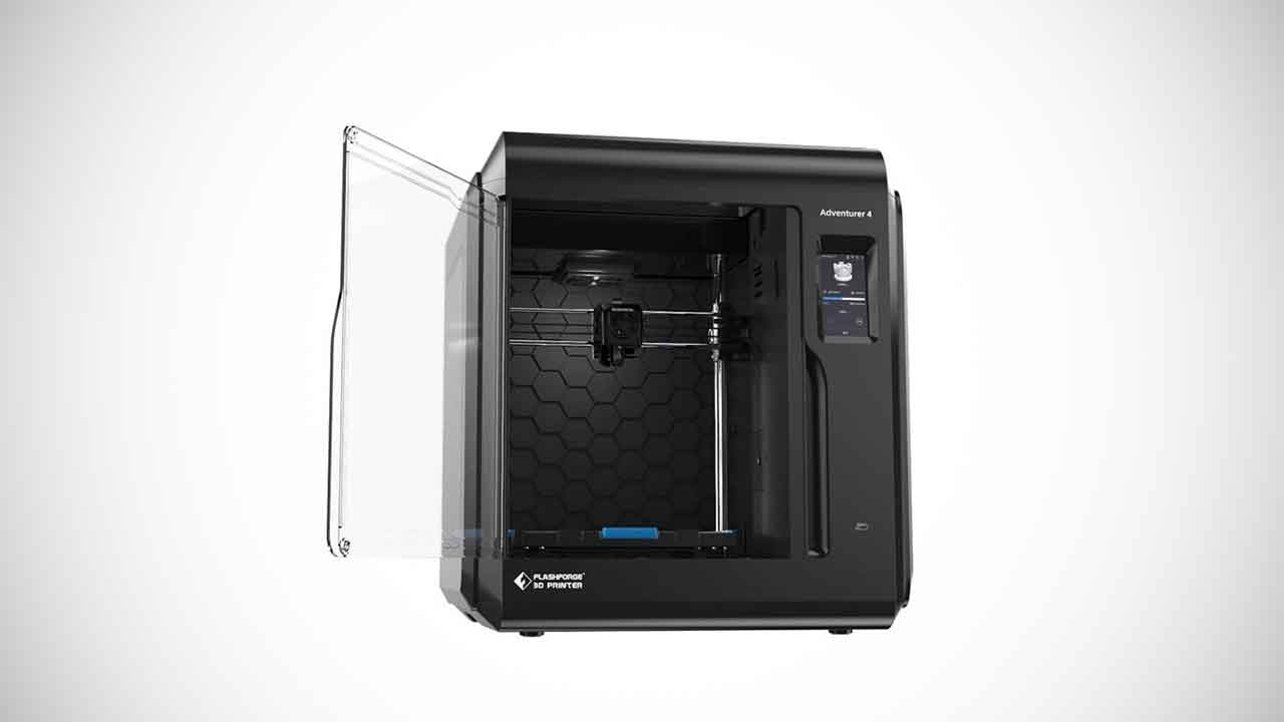

FlashForge Adventurer 4 can be said as the best intermediate 3D FFF printer.
Beyond the use of beginners in 2023 top 5 list FlashForge Adventurer 4 makes its place as it provides fuss-free printing with negating unnecessary interruptions and complications.
Small-businesses can buy this 3D printer.
Adventurer 4 features swappable print nozzles that controls the layer size and thickness for printing and also controls varied temperatures.
This 3D printer can be among the most flexible 3D printers as it can handle a wide variety of printing material.
Spend no hefty amount for this 3D printer and get good quality print with the average printing speed at ₹87,512.
SPECIFICATIONS
Printer Type: FFF
Layer Resolution: 0.1-0.4mm
Materials: ABS, PLA, PC, PETG, PLA-CF, PETG-CF
Build Volume: 9.8 x 8.6 x 7.9 inches
Printer Size / Weight: 21.3 x 19.7 x 18.5 inches / 57.3 pounds
| PROS | CONS |
|
|
Priced at: ₹87,512
When is the right time to buy a 3D printer?

3D printers are not in their early fame period, industries have realized the precision it brings to the project and in the object production.
In the past where using the 3D printers was optional or only available to selected sectors, now 3D printers have widened their variants and can be used in different sectors and cater to different sizes of organizations.
Besides, the advanced safety features, including power loss protection and filament runout sensors can be obtained and fixed via budget friendly options.
Why are 3D Printers an Important part of the Future?

A 3D printer can provide the flexibility, speed, and precision while manufacturing a 3D object.
This Additive manufacturing is extensively used across numerous sectors for rapid prototyping.
With the cut-throat competition, prototypes that companies need should be created in a matter of hours, as no months and years can only be invested in preparing a model and putting heavy money in R&D activities.
As claimed by most of the businesses, the prototyping process has just become 10 times easier and faster by inculcating 3D printers to the process.
3D printers are now used beyond prototyping and play a part virtually in all sectors. With futuristic ideas and designs, along with the advancement in 3D printing this can be said 3D printers are very much the part of the future in producing and creating 3 dimensional objects and catering to numerous sectors.
Conclusion
3D printers might as well be here to stay and with the different types of 3D printers coming to the market the choice needs to be coherent and conducive to the main aim of the business.
FAQ on 3D printers
Q.1 What setting is the best for 3D printers?
Ans. 1 Most 3D printers include or link to recommended software, which can handle converting 3D STL or other files into formats supported by the printer.
Stick with the suggested presets to start, with one exception. I’ve started adding a raft, or bottom layer of filament, to nearly everything I print.
It has cut down dramatically on prints that don’t adhere to the bed properly, which is a common issue.
If you continue to have problems, rub a standard glue stick on the print bed right before printing.
Q.2 What does ‘support’ stands for and it’s association with 3D printers?
Ans.2 Your 3D models probably need some help to print properly, as these printers don’t do well with big overhangs — for example, an arm sticking out from a figure.
Your 3D printer software can usually automatically calculate and add supports, meaning little stands that hold up all those sticking-out parts of the model.
After the print is done, clip the supports off with micro cutters and file down any nubs or rough edges with hobby files.
Q.3 What material can be the best for 3D printers?
Ans. 3 Most home 3D printers use PLA or ABS plastic. Professional printers can use all sorts of materials, from metal to organic filament.
Some printers use a liquid resin, which is much more difficult to handle but offers sharper details.
As a beginner, use PLA. It’s non-toxic, made mostly of cornstarch and sugarcane, handled easily, and is inexpensive.
However, it’s more sensitive to heat, so don’t leave your 3D prints on the dashboard of a car on a hot day.
Q.4 Two major types of 3D printers?
Ans.4 There are two types of 3D printers, including FFF (fused filament fabrication) and SLA (stereolithography).
FFF printers work by melting and molding plastic filament to create the object with a moving printhead.
Whereas, SLA printers employ UV lasers to harden the resin that solidify the model.
FFF printers are relatively cheaper than the SLA printers, not only cheaper but easy to use and simple.
Also Read: Flipkart Big Diwali Sale October 2022: Best Deals on Mobile Phones and Electronics
Also Read: Samsung Electronics Eyes Mass Production; Chip Manufacturing
and many more from this material.
Metal Filament: made of ground metals and polymer glue, available in steel, brass, copper , and bronze to produce the metal object with true look.
Wood Filament: The filament is made of polymer glue that is finely mixed with ground wood powder to produce wooden-looking objects.
Processes and Techniques of 3D Printing

There are some of the techniques of 3D printing used widely across diverse sectors. The techniques are as follows:
Stereolithography (SLA) Technology
SLA technology is used to create intricate and detailed objects, as well as supports fast prototyping printing. An ultraviolet laser is used to produce the objects in less time.
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
FDM technology is among the vastly adopted technologies for 3D printing. Majorly used to create the models and prototypes with plastic.
Digital Light Processing (DLP)
DLP technology uses lamps to generate the prints at higher speed as compared to SLA printing, as it allows the layers to dry in no time. It is also the oldest form of 3D printing.
Material Jetting
Material jetting technique uses droplets of material by small diameter nozzle to build a layer- to- layer platform, the object becomes strong due to the UV light used.
Continuous Liquid Interface Production (CLIP)
The CLIP method uses Digital Light Synthesis technology to preview the sequence of UV images for the cross-section 3D printed part. This method enables the curing process to have precise control. This process causes numerous chemical reactions that allow the layers to harden.
Binder Jetting
For Binder Jetting technique powder base material is used along with the liquid binder that act as an adhesive for the powder particles and are released via jet nozzles.
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
FDM is also known as Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF). This technique works by unwinding a plastic filament that flows through the heated nozzle in vertical and horizontal directions. This way it immediately forms the object by hardening the melted material.
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
SLS technique works by fusing small particles of powder together via high-power laser to build 3D objects. The laser scans the layers formed via powderbed and selectively fuses them, which lowers the powder bed by one layer and repeats the process until getting the desired thickness.
Multi-Jet Fusion (MJF)
MJF is another form of Powder Bed Fusion as it uses a sweeping arm that enables the deposit of powder and the application of inkjet-equipped arm for selective binding.
Moreover, there is a detailing agent that is used for the precision of the object. Also, there is utilization of thermal energy to cause the chemical reaction.
Directed Energy Deposition
Majorly used in the metal industry, Directed Energy Deposition technique operates on the 3D printing apparatus attached to a nozzle for applying the powder and a multi-axis robotic arm.
The application of the powder on the surface and energy source that melts the material that creates solid objects.
How to choose the best printer for your business?

Any business choosing the right 3D printer is based on a few parameters. The parameters for the same are as follows:
Printer type
There are two types of 3D printers, including FFF (fused filament fabrication) and SLA (stereolithography).
FFF printers work by melting and molding plastic filament to create the object with a moving printhead.
Whereas, SLA printers employ UV lasers to harden the resin that solidify the model.
FFF printers are relatively cheaper than the SLA printers, not only cheaper but easy to use and simple.
Printing Materials
The printing material varies for each type of printer.
FFF filament material includes PLA (a brittle, biodegradable material), HDPE (a light, tough polystyrene), ABS (the same plastic used in Lego blocks), and TPE (a soft, rubberlike material). Where the availability of PLA and ABS are in various colors and hues.
SLA printers comparatively function on fewer options.
However, the SLA printers are well equipped to form the objects from very rigid to rubbery.
The best 3D printers are those that can apply a wide range of material to form an object with desired degree of rigidity.
Note that: There are some 3D printers that allow the use of some material that is approved and produced by the respective manufacturer of the printers.
Print Volume
Determine the print volume before buying a 3D printer. As all printers come with certain limits on the basis of size of the object can be created.
The print bed decides the size of the print, which is measured by the cubic inches. Also look into the individual dimensions to ascertain the production of the maximum size 3D print.
Print Speed and Quality
Currently, 3D printing requires time to create the object, as produced in layers and the model design can vary from simple to complex.
The typical 3- to 4-inch design takes around 6 and 12 hours to create the object. Thicker the layers, quicker the print. The speed is also based on the print quality of the object.
Price
The 3D printers used by professional designers and creators can be of a heavy price.
However, the best 3D printers can also come at a budget-friendly price.
For the same read ahead to the top best 3D printers of 2023 that will be economical too.
Note that: There are some 3D printer producers that do not enroll their product on Amazon or any e-commerce platform. The users can also buy the product directly through the company;s website as well.
Top 5 3D Printers of 2023
Monoprice Voxel

Monoprice Voxel 3D printer, not too expensive as a 3D printer and do the task with presion.
This printer produces high quality prints and doesn’t hit the pocket badly as it is priced at Rs. 30,463.00.
Beginners can choose this printer as it can produce reliable prints by using ABS material and due to the heated print base on Monoprice Voxel.
The print bed’s top slides out and is flexible catering to remove prints fast.
Voxel can be a good choice for home or a classroom to meet the objective of the purchase.
SPECIFICATIONS
Printer Type: FFF
Layer Resolution: 50 to 400 microns
Materials: ABS, PLA, Wood Fill, Copper Fill, Steel Fill, Bronze FillBuild Volume: 6.9 x 6.9 6.9 inches
Printer Size / Weight: 15.9 x 15.7 x 15 inches / 19.8 pounds
| PROS | CONS |
|
|
Priced at: Rs. 30,463.05
Prusa Mini+

The Prusa Mini+ 3D printer can be the just the right fit for many beginners as it produces an excellent print quality and offers maximum reliability.
However, it is more expensive than its counterparts as it will be priced at Rs. 40,000.
Practically speaking, the Prusa Mini+ 3D printer is easy to set up but doesn’t have an enclosed printing space, which can be a problem if set around children.
The printer has a top-notch software prone to produce good quality objects from the model provided.
Moreover, the print speed is fast at 0.2mm quality print mode. Along with the material used in the printer it also makes the printer a reliable choice.
SPECIFICATIONS
Printer Type: FFF
Layer Resolution: 0.05 to 0.25 mm
Materials: PLA, PETG, ABSBuild Volume: 7 x 7 x 7 inches
Printer Size / Weight: 15 x 13 x 12.6 inches / 11 pounds
| PROS | CONS |
|
|
Priced at: Rs. 40,000
Formlabs Form 3+

Coming with a host of things, including Form 3+ 3D Printer, Form 3 Resin Tank V2.1, Build Platform, and Form 3 Finish Kit.
Formlabs Form 3+ printer will be priced at $3,750.00.
Resin based, SLA Form 3+ printer can be part of the regular workflow. This new version comes with better printing and easier to use.
Resin setup is also an easy task as well as the floating level sensor provides the exacts of the resin present in the tray.
Flexible build platform ensures the simplified task of removing prints.
Along with the advanced software system the printer can be a good pick.
SPECIFICATIONS
Printer Type: SLA
Layer Resolution: 25 to 300 microns
Materials: Resin
Build Volume: 7.3 x 5.7 x 5.7 inches
Printer Size / Weight: 20.9 x 15.9 x 14.8 inches / 38.5 pounds
| PROS | CONS |
|
|
Priced at: $3,750.00
Photon Mono X

Possibly the best pick for a budget-friendly SLA printer, as Photon Mono X is priced at Rs. 45,000. Compared to the Form 3, Photon Mono X is way more reasonable.
The results are also more than impressive and creates high-quality SLA prints, despite the sporadic printing error.
With the printing area of 331 cubic inches, providing a large printing area that can be a good-fit home workshop or small organizations.
And have no restriction on approving the resin.
SPECIFICATIONS
Printer Type: SLA
Layer Resolution: 0.01-0.15mm
Materials: Resin
Build Volume: 9.6 X 7.5 X 4.6 inches
Printer Size / Weight: 18 X 11.4 X 10.6 inches / 23.7 pounds
| PROS | CONS |
|
|
Priced at: Rs. 45,000
FlashForge Adventurer 4

FlashForge Adventurer 4 can be said as the best intermediate 3D FFF printer.
Beyond the use of beginners in 2023 top 5 list FlashForge Adventurer 4 makes its place as it provides fuss-free printing with negating unnecessary interruptions and complications.
Small-businesses can buy this 3D printer.
Adventurer 4 features swappable print nozzles that controls the layer size and thickness for printing and also controls varied temperatures.
This 3D printer can be among the most flexible 3D printers as it can handle a wide variety of printing material.
Spend no hefty amount for this 3D printer and get good quality print with the average printing speed at ₹87,512.
SPECIFICATIONS
Printer Type: FFF
Layer Resolution: 0.1-0.4mm
Materials: ABS, PLA, PC, PETG, PLA-CF, PETG-CF
Build Volume: 9.8 x 8.6 x 7.9 inches
Printer Size / Weight: 21.3 x 19.7 x 18.5 inches / 57.3 pounds
| PROS | CONS |
|
|
Priced at: ₹87,512
When is the right time to buy a 3D printer?

3D printers are not in their early fame period, industries have realized the precision it brings to the project and in the object production.
In the past where using the 3D printers was optional or only available to selected sectors, now 3D printers have widened their variants and can be used in different sectors and cater to different sizes of organizations.
Besides, the advanced safety features, including power loss protection and filament runout sensors can be obtained and fixed via budget friendly options.
Why are 3D Printers an Important part of the Future?

A 3D printer can provide the flexibility, speed, and precision while manufacturing a 3D object.
This Additive manufacturing is extensively used across numerous sectors for rapid prototyping.
With the cut-throat competition, prototypes that companies need should be created in a matter of hours, as no months and years can only be invested in preparing a model and putting heavy money in R&D activities.
As claimed by most of the businesses, the prototyping process has just become 10 times easier and faster by inculcating 3D printers to the process.
3D printers are now used beyond prototyping and play a part virtually in all sectors. With futuristic ideas and designs, along with the advancement in 3D printing this can be said 3D printers are very much the part of the future in producing and creating 3 dimensional objects and catering to numerous sectors.
Conclusion
3D printers might as well be here to stay and with the different types of 3D printers coming to the market the choice needs to be coherent and conducive to the main aim of the business.
FAQ on 3D printers
Q.1 What setting is the best for 3D printers?
Ans. 1 Most 3D printers include or link to recommended software, which can handle converting 3D STL or other files into formats supported by the printer.
Stick with the suggested presets to start, with one exception. I’ve started adding a raft, or bottom layer of filament, to nearly everything I print.
It has cut down dramatically on prints that don’t adhere to the bed properly, which is a common issue.
If you continue to have problems, rub a standard glue stick on the print bed right before printing.
Q.2 What does ‘support’ stands for and it’s association with 3D printers?
Ans.2 Your 3D models probably need some help to print properly, as these printers don’t do well with big overhangs — for example, an arm sticking out from a figure.
Your 3D printer software can usually automatically calculate and add supports, meaning little stands that hold up all those sticking-out parts of the model.
After the print is done, clip the supports off with micro cutters and file down any nubs or rough edges with hobby files.
Q.3 What material can be the best for 3D printers?
Ans. 3 Most home 3D printers use PLA or ABS plastic. Professional printers can use all sorts of materials, from metal to organic filament.
Some printers use a liquid resin, which is much more difficult to handle but offers sharper details.
As a beginner, use PLA. It’s non-toxic, made mostly of cornstarch and sugarcane, handled easily, and is inexpensive.
However, it’s more sensitive to heat, so don’t leave your 3D prints on the dashboard of a car on a hot day.
Q.4 Two major types of 3D printers?
Ans.4 There are two types of 3D printers, including FFF (fused filament fabrication) and SLA (stereolithography).
FFF printers work by melting and molding plastic filament to create the object with a moving printhead.
Whereas, SLA printers employ UV lasers to harden the resin that solidify the model.
FFF printers are relatively cheaper than the SLA printers, not only cheaper but easy to use and simple.
Also Read: Flipkart Big Diwali Sale October 2022: Best Deals on Mobile Phones and Electronics
Also Read: Samsung Electronics Eyes Mass Production; Chip Manufacturing
