Highlights
- Surge in generative AI systems has revolutionsed image creation and editing
- However risks of unauthorised manipulation and theft of online artworks loom large.
- MIT CSAIL introduces “PhotoGuard,” a novel approach using encoder and diffusion attack methods.
- Collaborative approach needed to tackle limitations and challenges in AI-driven image protection.
The surge in generative AI systems like Dall-E and Stable Diffusion has led to groundbreaking capabilities in creating and editing images.
Companies like Shutterstock and Adobe are at the forefront of this revolution.
But these new abilities are accompanied by familiar challenges, such as unauthorised manipulation or outright theft of online artwork and images.
Techniques to tackle these problems are emerging, such as watermarking and the innovative “PhotoGuard” method developed by MIT CSAIL.
Growing Potential and Risks of Generative AI

The world of generative AI is expanding, allowing chatbots across the internet not only to create images but also to edit them.
This development comes as part of an effort by companies to distinguish their products from those of their competitors, opening new possibilities and conveniences in the field of digital media.
With these advancements, however, come significant risks.
Unauthorised manipulation and outright theft of existing online artworks and images pose a major concern.
Protection techniques are needed to maintain integrity and originality.
Watermarking is a conventional method employed to counter image theft.
It serves as a deterrent by marking images with a recognisable pattern or logo, identifying the original source.
So what does PhotoGuard do?

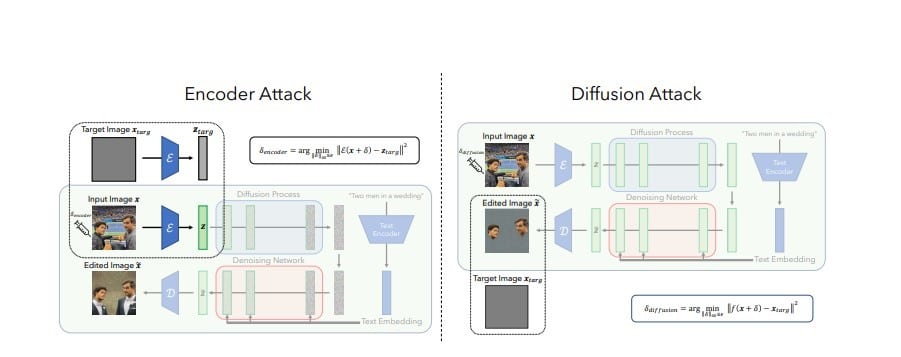
MIT CSAIL’s “PhotoGuard” goes a step further by altering select pixels in an image to disrupt an AI’s understanding of it.
The research team uses “perturbations” invisible to human eyes but readable by machines.
The application initiates an “encoder” attack method that targets the algorithmic model’s latent representation, preventing the AI from recognising the image.
This method essentially confuses the AI’s interpretation of the image’s properties.
Apart from that PhotoGaurd is also capable of a more complex “diffusion” attack method that camouflages an image as a different image to the AI.
It optimises the perturbations in its image to resemble its target, leading to unrealistic-looking generated images when edited by the AI.
What are the limitations?
Although promising, PhotoGuard isn’t foolproof.
Malicious actors might reverse engineer the protected image by adding digital noise or altering the image.
The lead author of the study, Hadi Salman, acknowledges the need for a “collaborative approach” involving various stakeholders to ensure robust defense.
Bleak future for Generative AI?

The emergence of AI-powered image editing capabilities marks a significant milestone in technology, but it also necessitates new measures to protect intellectual property.
Innovations like PhotoGuard highlight the ongoing efforts to strike a balance between leveraging AI’s potentials and safeguarding original artwork.
Continued investment and collaboration among companies, platforms, and policymakers will be key to achieving practical solutions to the challenges posed by these AI tools.
FAQs
Ques) What are the advancements in generative AI for image creation and editing?
Ans) Generative AI has allowed chatbots across the internet to create and edit images, with major companies like Shutterstock and Adobe leading the way. New techniques are opening opportunities in digital media, but also raising concerns about unauthorised manipulation and theft of images.
Ques) How does PhotoGuard work, and what makes it innovative?
Ans) PhotoGuard, developed by MIT CSAIL, disrupts an AI’s understanding of an image by altering select pixels, using methods called encoder and diffusion attacks. These attacks confuse the AI’s interpretation of the image or make it see a different image, protecting against unauthorised editing.
Ques) What are the limitations of PhotoGuard, and how can they be addressed?
Ans) PhotoGuard is not entirely foolproof, as malicious actors might reverse engineer the protected image. Collaborative efforts involving model developers, social media platforms, and policymakers are required to ensure robust defense and make this protection practical.
Ques) Does the advent of AI-powered image editing mean a bleak future for digital artistry?
Ans) The emergence of AI in image editing is a significant technological milestone but necessitates measures to protect intellectual property. With innovations like PhotoGuard and continued collaboration, there’s an ongoing effort to balance AI’s potential with the safeguarding of original artwork.
Also Read: Artificial Intelligence And Its Applications In The Real World?
Also Read: OpenAI DALL-E Image Generator; Human Face Editing Made Easy








