Highlights
- Developed by the US Department of Defense in the 1970s, now integral to global navigation.
- Works through a constellation of satellites, enabling precise location tracking.
- Essential for real-time navigation, timing, and geofencing applications.
- Owned and operated by the US, but serves as a free global utility.
The Global Positioning System (GPS) is a cornerstone of modern navigation and tracking technology.
It comes as little surprise that the technology is an integral part of countless applications from driving directions to global commerce.
How was GPS first conceptualised?
Who owns GPS?
How does it work?
This deep dive into GPS location services provides a comprehensive overview of a system that has become indispensable in our daily lives.
Conception and Development
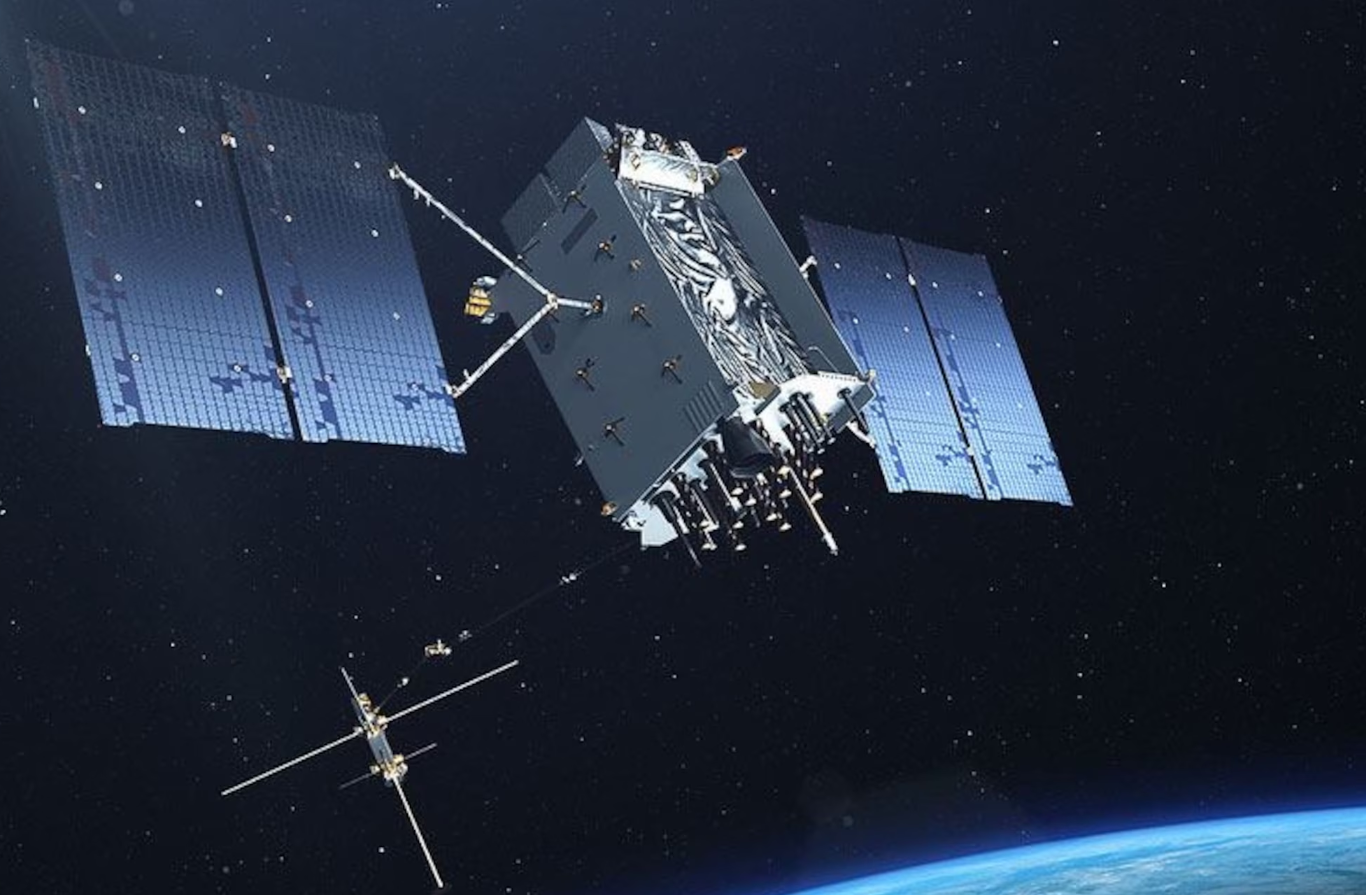

GPS was developed by the United States Department of Defense in the 1970s, with the first satellite launched in 1978.
Originally intended for military applications, it was made available for civilian use in the 1980s.
The system reached full operational capability in 1995, marking the beginning of a new era in navigation technology.
Since then the technology has become highly integral in everything from smartphones to cars.
How Does GPS Work?
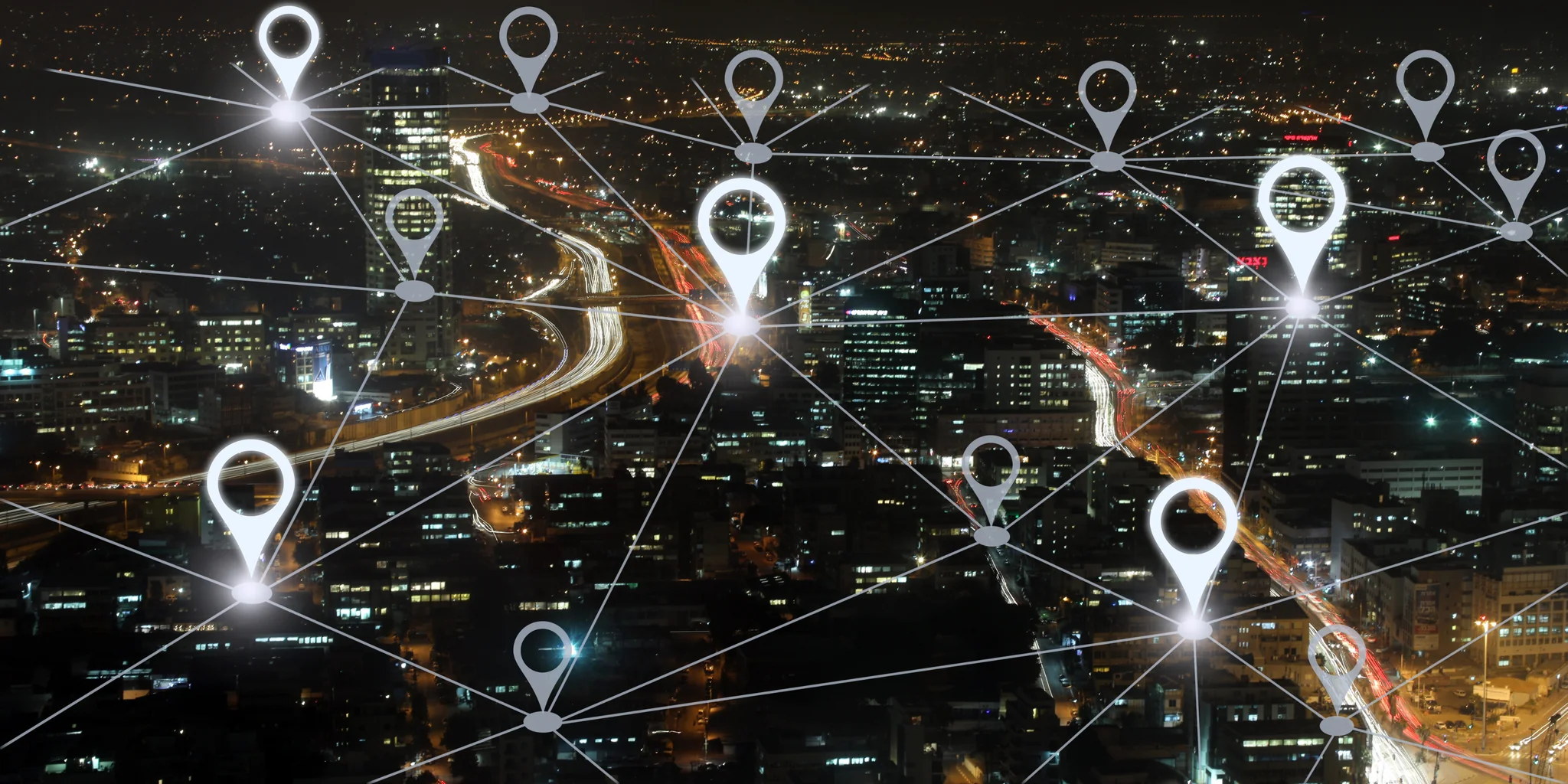

GPS operates through a constellation of at least 24 satellites orbiting the Earth, transmitting signals to receivers on the ground.
These receivers calculate their precise location (latitude, longitude, and altitude) by analyzing the signals received from at least four GPS satellites.
The calculation involves measuring the time each signal takes to reach the receiver, allowing it to determine the distance from each satellite and thereby pinpoint its location on Earth through a process known as trilateration.
Key Features and Applications
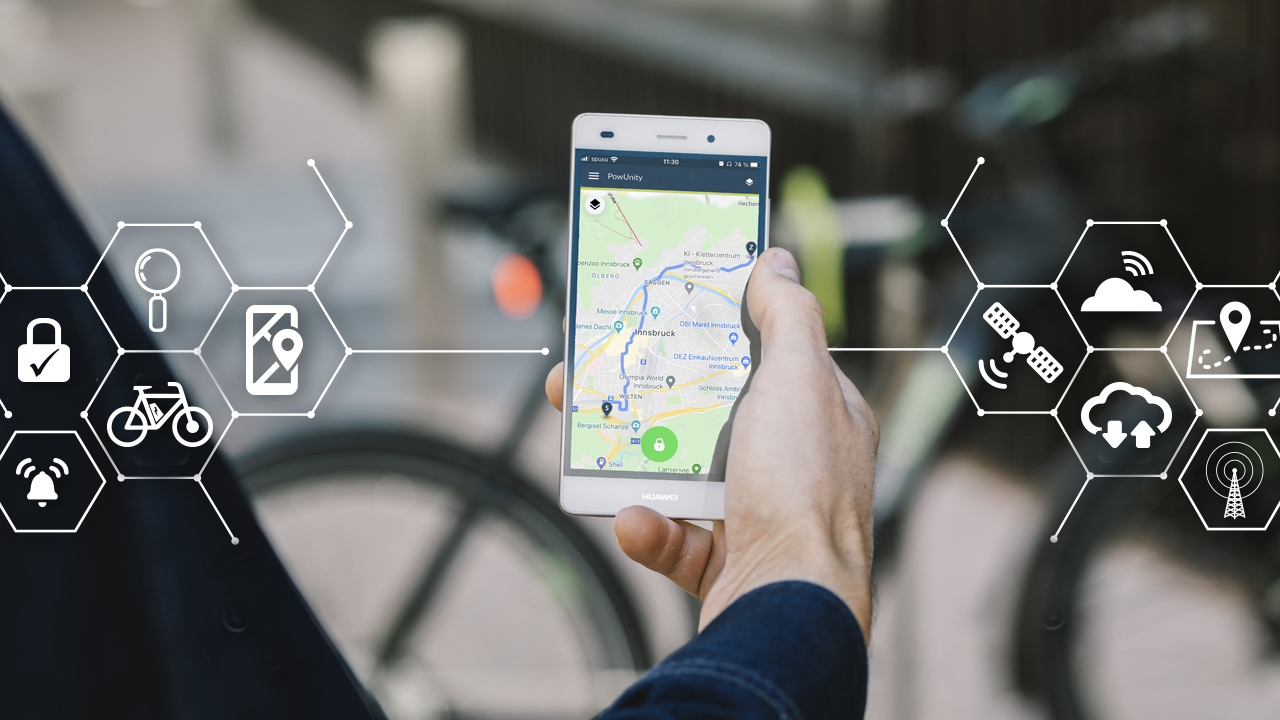
- Real-time navigation: GPS provides real-time position and velocity information, essential for navigation in cars, planes, and ships.
- Location tracking: It enables tracking of objects and individuals, useful in logistics, wildlife monitoring, and personal safety devices.
- Timing: GPS offers precise timing signals, critical for time-sensitive operations like stock trading, electrical grid management, and telecommunications.
- Geofencing: This feature allows for the creation of virtual geographic boundaries, triggering a response when a device enters or leaves a particular area.
Control and Maintenance
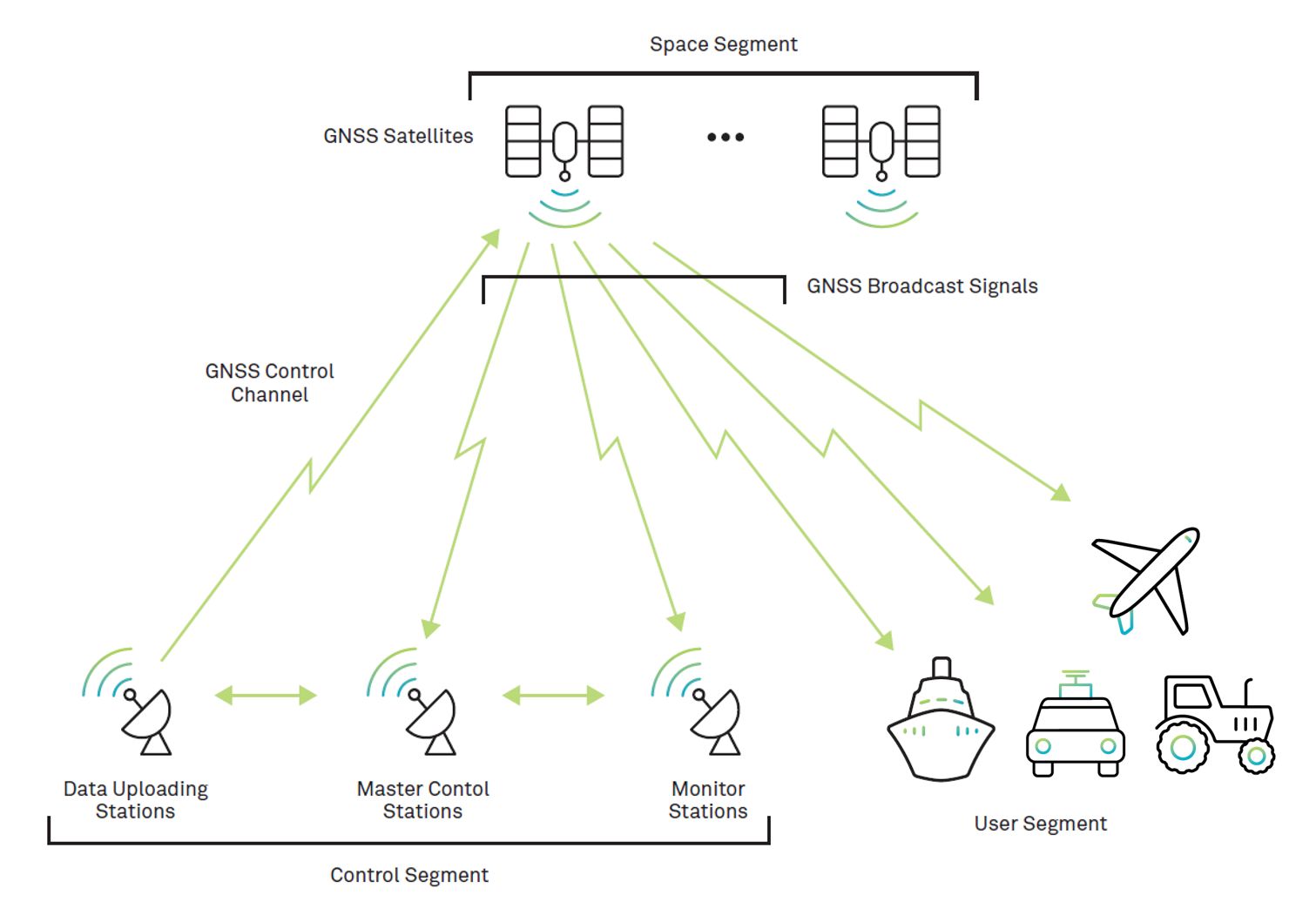
The GPS is owned by the United States government and operated by the United States Space Force.
It is provided as a global utility free of charge, although the infrastructure and maintenance are funded by American taxpayers.
Despite its US ownership, GPS is a global system that serves users worldwide without discrimination.
This also means that if the US so desires, can take away this service from every other nation on the planet.
Benefits of GPS

- Enhanced Safety: GPS plays a critical role in emergency response, search and rescue operations, and disaster relief by enabling rapid and accurate location tracking.
- Economic Impact: It significantly contributes to the global economy by boosting efficiency in transportation, logistics, and agriculture, among other sectors.
- Accessibility: GPS technology has made navigation and location-based services accessible to millions of users globally, enhancing personal mobility and convenience.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite its widespread adoption, GPS faces challenges such as signal interference, spoofing, and the need for greater accuracy in dense urban environments.
The future of GPS is likely to include advancements like the integration of additional satellites, improved signal strength, and compatibility with other global navigation satellite systems (GNSS) like Europe’s Galileo, Russia’s GLONASS, and China’s BeiDou.
India is also in the fray with NaVIC satellite working to provide location services in India.
FAQs
What is GPS and who developed it?
GPS, or Global Positioning System, is a navigation system developed by the United States Department of Defense in the 1970s to provide precise location and time information globally.
How does GPS determine my location?
GPS determines your location using signals from at least four satellites. By measuring the time it takes for each signal to reach the receiver, it calculates your exact position through trilateration.
Is GPS free to use?
Yes, GPS is provided as a free global utility by the United States government, although its maintenance and infrastructure are funded by American taxpayers.
Can GPS be used for more than just navigation?
Absolutely, GPS is crucial for a variety of applications beyond navigation, including location tracking, precise timing for financial transactions, electrical grids, and creating geofenced areas for security purposes.
What challenges does GPS face, and what is its future?
GPS challenges include signal interference and the need for higher accuracy in urban areas. Future advancements may include additional satellites, enhanced signal strength, and better integration with other global navigation satellite systems.
What are the Types of GPS in mobile phone industry ?
A-GPS (Assisted GPS) – this type of GPS is used to speed up the start-up time of the GPS based positioning systems.
The A-GPS would assist the receiver in getting a lock when the signal is weak. For this to work, though, a network connection is required in the mobile phone because the A-GPS uses the assistance server to get the lock.
S-GPS (Simultaneous GPS) – it is a method to enhance the satellite-based reporting ability to a network carrier.
The S-GPS allows a cell phone to receive both GPS and Voice Data at the same time, thus improving the sensitivity and allowing the network providers to give services based on the location.
How GPS supports assured position, navigation and timing?
GPS was one of the first established satellite positioning systems and its innovations continue to support the growth and adoption of positioning technologies today.
As GPS-based autonomous applications become more common, GPS will also continue to be at the core of everyday life.
Also Read: How to Track Friends Live Location through Google Maps?
Also Read: Introducing Qubo’s Latest GPS Trackers and Dashcam Models: Advanced Tech for Cars & Bikes
