HIGHLIGHTS
* The Galaxy S23 Ultra’s moon photo debate is back again.
* This time it’s on Twitter and in a rather funny way.
* A Community Note on Twitter has flagged the Galaxy S23 Ultra’s moon feature as “fake”.
It looks like the debate over Galaxy S23 Ultra’s moon photos isn’t over yet. Despite explaining how the Galaxy S23 Ultra is capable of capturing clear moon photos with 100x zoom, people don’t seem to be convinced. And this time it’s even worse as Twitter itself has flagged the Galaxy S23 Ultra’s moon photos as “fake”.

Samsung has been running an ad on Twitter about the Galaxy S23 Ultra’s moon capturing capabilities. The Twitter ad reads, “There is no dark side of the moon with the #GalaxyS23Ultra. Capture your night skies and share with us by replying to this thread with #SharetheEpic.”
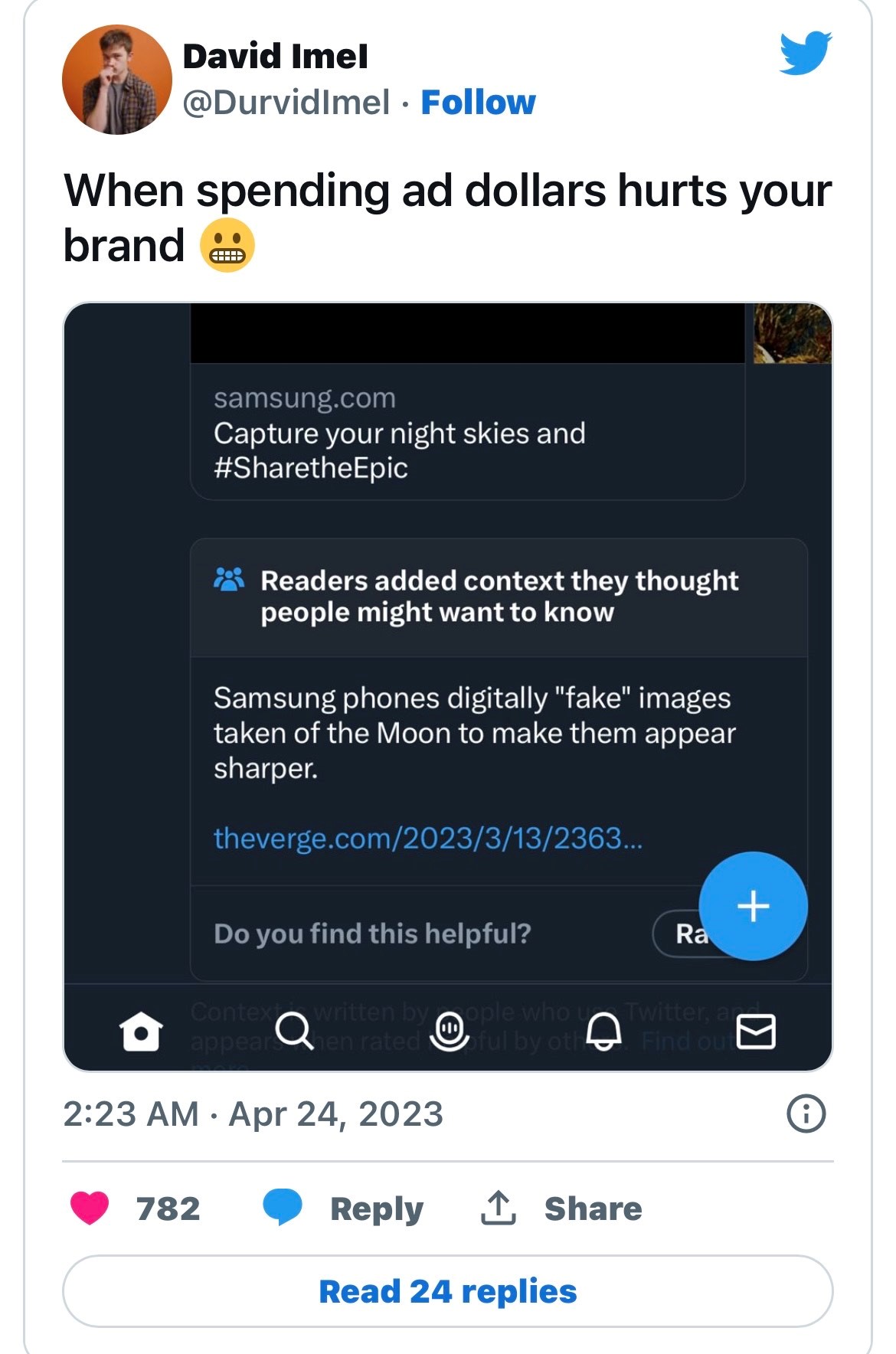
Just below the ad, there’s a Twitter Community Note that says, “Samsung phones digitally “fake” images taken of the Moon to make them appear sharper.” For those unaware, Community Notes are essentially fact checking information provided by contributors on Twitter.
Contributors have the liberty to add notes on any tweet and if the required number of contributors rate that note as helpful, then Twitter will publicly show it below the tweet.
Just like how contributors can add notes below tweets, anyone can report it, and the tweet author can also request for additional review. But considering how this particular note appears on an ad that Samsung paid for, it’s somewhat ironical. You may not see the ad right now but one David ImeI took a screenshot and shared it on Twitter.
Galaxy S23 Ultra Moon Photos

Coming back to whether the moon photos captured by the Galaxy S23 Ultra indeed are real or not – Samsung has already denied such allegations. Yes, there is some work done inside to produce those clear images but what Samsung says is that it doesn’t add any image overlay.
It’s a mix of multiple things working together by using advanced technologies to get the highest resolution image and it’s further enhanced by using Al to get the final result which is a clear image of the moon.

The Community Note on Twitter probably meant that but the explanation behind the moon photos can get more complex. Community Notes are currently available only in select countries including the US, UK, Ireland, Australia, and New Zealand. So it’s very likely that you won’t see the note on Twitter.
Samsung details how its moon photos work with Scene Optimizer Feature

Samsung has now responded to these accusations by explaining how its moon photos work and why they aren’t completely fake. They use super resolution technologies and AI technology to produce high-quality moon images. The phone doesn’t apply any image overlaying to the photos; instead, the AI-based scene optimization technology recognizes the moon as the main object and takes multiple shots for multi-frame composition.
Samsung Scene Optimizer Feature

Samsung’s Scene Optimizer feature uses advanced AI to recognize objects and provide the best results to users. With the Galaxy S21 series, the camera now recognizes the moon as a specific object during photo-taking and enhances details using its detail enhancement engine.
The camera system utilizes deep learning-based AI technology and multi-frame processing to further enhance details when taking photos of the moon. Learn more about the steps, processes, and technologies involved in capturing high-quality images of the moon.
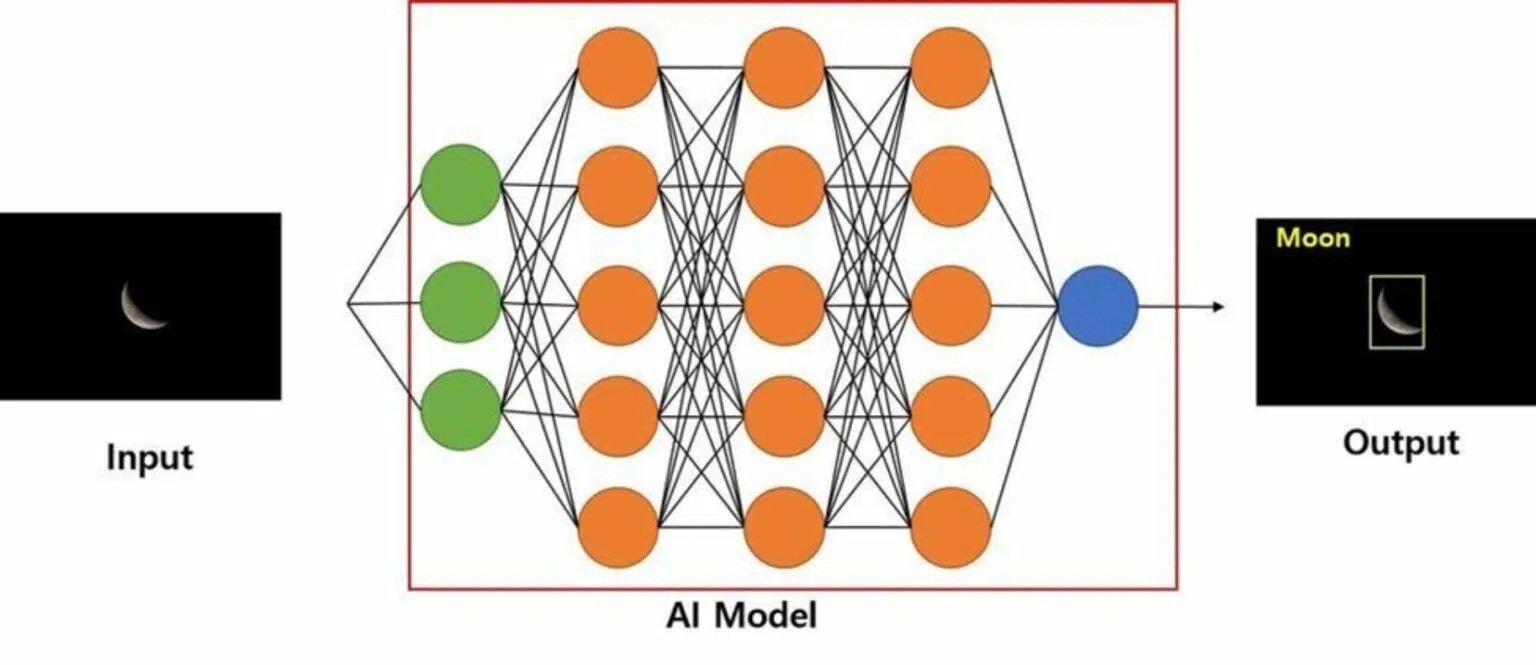
AI Deep Learning for Moon Object Recognition
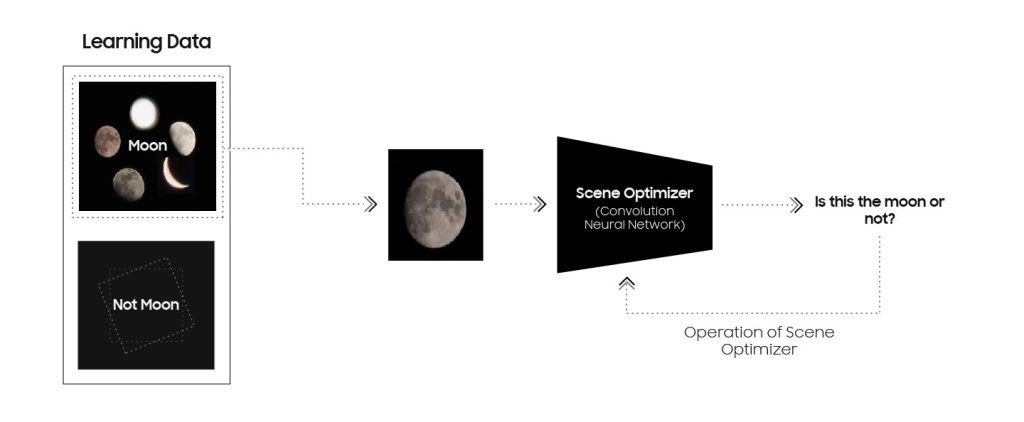
Samsung has developed an AI engine capable of recognizing the moon in various shapes and details, from full to crescent. It uses a deep learning model to detect the presence and location of the moon in images taken from Earth.
The AI model continues to learn and can recognize the moon even in images that were not used in training. With a simple square box denoting the area occupied by the moon, this technology is set to revolutionize the way we view and study the moon.
The Brightness Control Process and Capturing the Most Stable Images Possible
Samsung has developed a process to capture the most stable and clear images of the moon. The device recognizes the moon and controls the display brightness to optimize clarity. Even in early evening, the device will darken the background to enhance the moon’s visibility.
The Zoom Lock feature reduces shaking effects without a tripod using OIS and VDIS technologies. It activates automatically when zooming in on the moon or maintaining focus for more than 1.5 seconds. The border and display change to yellow, locking the moon in place for truly epic shots.
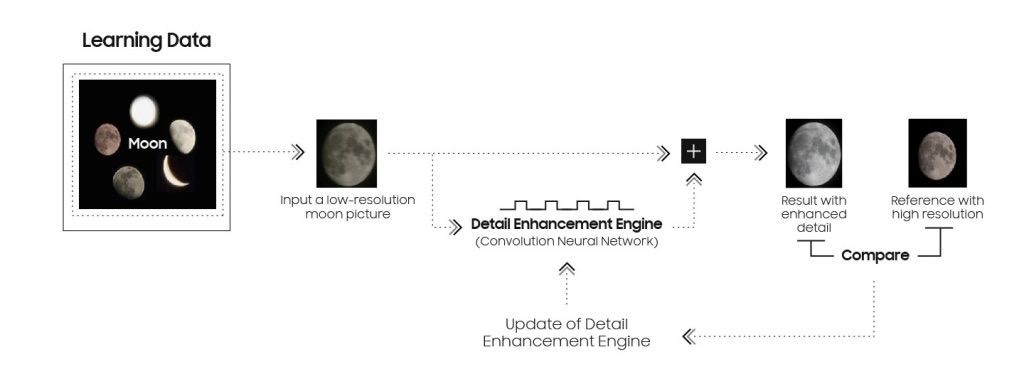
Samsung’s AI Powered Detail Enhancement to Capture the Moon
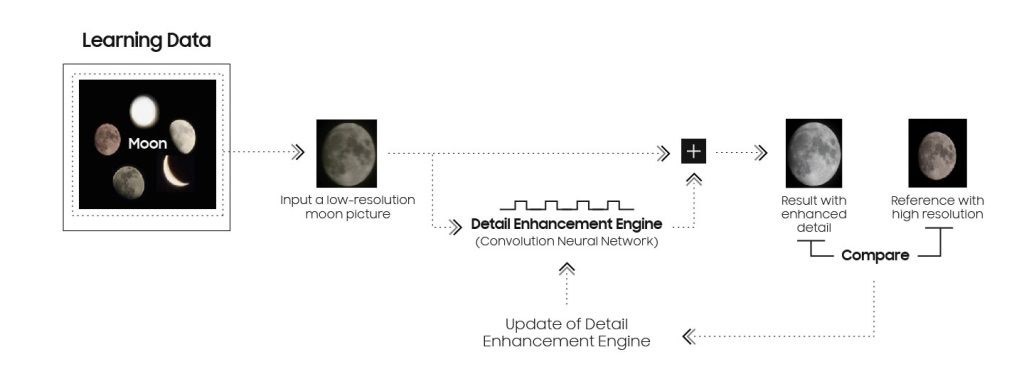
Samsung’s Galaxy device allows users to capture a bright and clear image of the moon. Once the moon reaches an appropriate brightness level, the user can press the capture button. The camera then utilizes Scene Optimizer to determine whether to apply the detail enhancement engine through AI processing.
Multiple pictures are taken and synthesized into a single, bright image with reduced noise through Multi-frame Processing.
Finally, the deep-learning-based AI detail enhancement engine of Scene Optimizer is used to eliminate remaining noise and enhance image details even further.
Scene Optimizer availability

Samsung’s Scene Optimizer is exclusively available on the Galaxy S20 and above models, as well as all Galaxy Z Fold series.
Explaining about AI Technology to Produce High-Quality Images of the Moon, Samsung, said Samsung continues to improve Scene Optimizer to reduce any potential confusion that may occur between the act of taking a picture of the real moon and an image of the moon.

Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra Key Specifications
Display & Storage
| RAM | 8 GB |
| Processor | Qualcomm Snapdragon 8 Gen 2 |
| Rear Camera | 200 MP + 12 MP + 10 MP + 10 MP |
| Front Camera | 12 MP |
| Battery | 5000 mAh |
| Display | 6.8 inches (17.27 cm) |
General
| Launch Date | February 1, 2023 (Unofficial) |
| Operating System | Android v13 |
| Custom UI | Samsung One UI |
Performance
| Chipset | Qualcomm Snapdragon 8 Gen 2 |
| CPU | Octa core (3.2 GHz, Single core, Cortex X3 + 2.8 GHz, Quad core, Cortex A715 + 2 GHz, Tri core, Cortex A510) |
| Architecture | 64 bit |
| Fabrication | 4 nm |
| Graphics | Adreno 740 |
| RAM | 8 GB |
| RAM Type | LPDDR5X |
Display
| Display Type | Dynamic AMOLED |
| Screen Size | 6.8 inches (17.27 cm) |
| Resolution | 1440 x 3088 pixels |
| Pixel Density | 501 ppi |
| Screen to Body Ratio (calculated) | 89.99 % |
| Screen Protection | Corning Gorilla Glass, Glass Victus |
| Bezel-less display | Yes with punch-hole display |
| Touch Screen | Yes, Capacitive Touchscreen |
| Brightness | 1750 nits |
| HDR 10 / HDR+ support | Yes, HDR 10+ |
| Refresh Rate | 120 Hz |
Design
| Height | 163.4 mm Compare Size |
| Width | 78.1 mm |
| Thickness | 8.9 mm |
| Weight | 223 grams |
| Build Material | Back: Gorilla Glass |
| Colours | Green |
| Waterproof | Yes, Water resistant (up to 30 minutes in a depth of 1.5 meter), IP68 |
| Ruggedness | Dust proof |
Camera
| MAIN CAMERA | ||
| Camera Setup | Quad | |
| Resolution | 200 MP f/1.7, Wide Angle, Primary Camera(23 mm focal length, 1.31″ sensor size, 0.6µm pixel size)12 MP f/2.2, Ultra-Wide Angle Camera(13 mm focal length, 2.55″ sensor size, 1.4µm pixel size)10 MP f/2.4, Telephoto Camera(70 mm focal length, 3.52″ sensor size, 1.12µm pixel size)10 MP f/4.9(230 mm focal length) | |
| Sensor | ISO-CELL | |
| Autofocus | Yes | |
| OIS | Yes | |
| Flash | Yes, LED Flash | |
| Image Resolution | 14500 x 13650 Pixels | |
| Settings | Exposure compensation, ISO control | |
| Shooting Modes | Continuous Shooting High Dynamic Range mode (HDR) |
|
| Camera Features | Digital Zoom Auto Flash Face detection Touch to focus |
|
| Video Recording | 7680×4320 @ 24 fps 3840×2160 @ 30 fps 1920×1080 @ 30 fps |
|
| FRONT CAMERA | ||
| Camera Setup | Single | |
| Resolution | 12 MP f/2.2, Wide Angle, Primary Camera(25 mm focal length) | |
| Autofocus | Yes, Phase Detection autofocus | |
| Video Recording | 3840×2160 @ 30 fps 1920×1080 @ 30 fps |
|
Battery
| Capacity | 5000 mAh |
| Type | Li-Polymer |
| Removable | No |
| Wireless Charging | Yes |
| Quick Charging | Yes, Fast, 45W |
| USB Type-C | Yes |
Storage
| Internal Memory | 256 GB |
| Expandable Memory | No |
| Storage Type | UFS 4.0 |
| USB OTG | Yes |
Network & Connectivity
| SIM Slot(s) | Dual SIM, GSM+GSM |
| SIM Size | SIM1: Nano, SIM2: Nano |
| Network Support | 5G Not Supported in India, 4G Supported in India, 3G, 2G |
| VoLTE | Yes |
| SIM 1 |
4G Bands:
TD-LTE 2600(band 38) / 2300(band 40) / 2500(band 41) / 1900(band 39)
FD-LTE 2100(band 1) / 1800(band 3) / 2600(band 7) / 900(band 8) / 700(band 28) / 1900(band 2) / 1700(band 4) / 850(band 5) / 850(band 18) / 850(band 19) / 1900(band 25) / 850(band 26) 3G Bands:
UMTS 1900 / 2100 / 850 / 900 MHz
2G Bands:
GSM 1800 / 1900 / 850 / 900 MHz
GPRS:
Available
EDGE:
Available
|
| SIM 2 |
4G Bands:
TD-LTE 2600(band 38) / 2300(band 40) / 2500(band 41) / 1900(band 39)
FD-LTE 2100(band 1) / 1800(band 3) / 2600(band 7) / 900(band 8) / 700(band 28) / 1900(band 2) / 1700(band 4) / 850(band 5) / 850(band 18) / 850(band 19) / 1900(band 25) / 850(band 26) 3G Bands:
UMTS 1900 / 2100 / 850 / 900 MHz
2G Bands:
GSM 1800 / 1900 / 850 / 900 MHz
GPRS:
Available
EDGE:
Available
|
| Wi-Fi | Yes, Wi-Fi 6 (802.11 a/b/g/n/ac/ax) 5GHz |
| Wi-Fi Features | Mobile Hotspot |
| Bluetooth | Yes, v5.3 |
| GPS | Yes with A-GPS, Glonass |
| NFC | Yes |
| USB Connectivity | Mass storage device, USB charging |
Multimedia
| FM Radio | No |
| Loudspeaker | Yes |
| Audio Jack | USB Type-C |
Sensors
| Fingerprint Sensor | Yes |
| Fingerprint Sensor Position | On-screen |
| Fingerprint Sensor Type | Ultrasonic |
| Other Sensors | Light sensor, Proximity sensor, Accelerometer, Compass, Gyroscope |
Faqs on Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra’s Moon
1) How do Samsung moon shots work?
Ans) Moon shots on Samsung phones use the periscope telephoto camera. But if we scientifically analyse this, there are two conflicting points of view. The moon is approximately 384,000km away.
The distance makes it difficult for even a 10X sensor to accurately capture all of the details. However, sensors are good at recognising bright objects. The moon is objectively the brightest object you see in the night sky.
The long-range periscope telephoto cameras capture really bright subjects easily. If you’re wondering why it’s easier to capture a moon at 50X or 100X than a swooping landscape at 30X, it’s because sensors can capture bright subjects better.
As a result, the images still retain organic detail despite the heavy crop-in. With smartphone cameras, half of the end result depends on image processing in these times.
Smartphone camera hardware is improving but is undeniably smaller than actual camera hardware. We’re only approaching the 1″ size for the main sensors. Most secondary sensors are still stuck at smaller than 1/2″ sizes.
Companies are currently prioritizing software X processing to maximize image quality as it is more challenging for them to frequently upgrade their hardware. Software is responsible for several image enhancements.
Software is responsible for artificial sharpening, noise reduction algorithms, choosing a target white and black point, setting the right ISO and shutter speed, reaching a balance with target exposure, and more.
Not to forget that software is entirely responsible for high dynamic range capture, where the software intelligently fuses multiple images taken at various exposure levels. It blends the images together into one evenly exposed shot with proper shadows (darker regions like trees or buildings) and highlights (bright skies and lights). Recently, Al recognition also started becoming rather popular.
2) Are the moon shots fake?
Ans) The Snapdragon 8 Gen 2 SOC’s ISP is a great example of Al recognition. Prior to this, Pixels could do it with their Custom ISPs.
Using Machine Learning algorithms, Al recognises everyday objects, hair, trees, skies, water bodies, etc. and fine-tunes these in the end result. As a result, the photos look much cleaner and more presentable. Some even have dedicated food modes.
Similar to the existing Al enhancements that are based on subject recognition, the moon is an easy subject to recognise for the built-in algorithms. It’s a combination of both Samsung’s software processing and the 8 Gen 2’s excellent new ISP. This is where the controversy about Samsung’s moon shots begins and ends. A new post on Reddit claims that Samsung’s moon shots are fake. There’s no clear-cut answer to this, but not all of the moon shots that come out of Samsung phones are fake.
There are two scenarios to consider. In the first, you point your phone at the sky, and it recognises the moon. Here, Samsung does not superimpose an artificial image of a pre-saved moon.
Once Al detects the tiny blob of light in the sky, it applies sharpness and locks the target exposure to the moon to make the shot look more presentable. It identifies the moon’s details, enhances them, and adds artificial texture to the real subject.
Samsung confirms the use of Al to enhance moon shots with the scene optimiser on.
Since it’s going through a machine-learning algorithm and improving image quality from training data, it’s not a fake photo.
Also Read: Realme 11 Pro+ Confirmed to Sport dedicated Moon Mode Ahead of Launch: Teaser Suggests
